How To Install Software Through Group Policy In Windows 2012
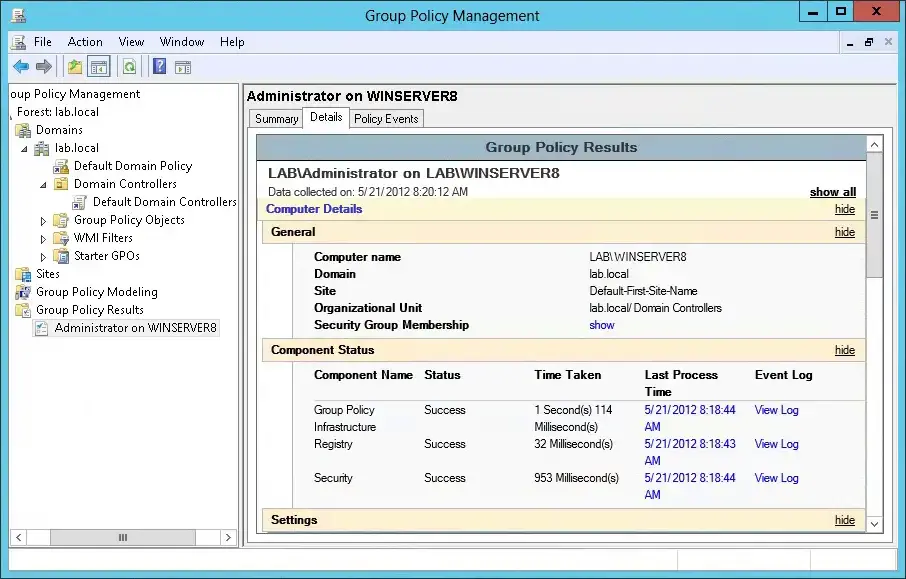 Grouping Policy is a feature of Windows Server using which admins can install software on all user computers. Information technology tin be done remotely without manual intervention. GPO is short for Group Policy. It becomes so popular amongst companies because it can make deployment clear and like shooting fish in a barrel due to the technology of group policy.
Grouping Policy is a feature of Windows Server using which admins can install software on all user computers. Information technology tin be done remotely without manual intervention. GPO is short for Group Policy. It becomes so popular amongst companies because it can make deployment clear and like shooting fish in a barrel due to the technology of group policy.
The GPSI feature is not available from the local Group Policy Object (i.e. past launching gpedit.msc). Microsoft did not implement this feature in the local GPO. Therefore, you'll need an Agile Directory installation to start using this feature. Once you've created a GPO using the Microsoft Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) or the AD Users and Computers MMC snap-in, edit that GPO to bring upwards the Group Policy editor MMC snap-in.
You tin can deploy software using GPSI as either a per-figurer or per-user deployment. The per-computer feature can exist establish in the GP editor under Computer Configuration\Software Settings\Software Installation (see Figure 1 below), while the per-user deployment feature is under User Configuration\Software Settings\Software Installation.
The best manner to deploy packages using GPSI is to apply the Distributed File Organisation (DFS) feature built into Windows Server. This features allows you to abstract the file path from the concrete location of the file and then that if you need to move application packages from 1 server to some other, the file path stored in the GPO for that package will not need to change. This is peculiarly important because the native GPSI feature does not support changing the packet path forexisting packages–you need to create a new packet, which has an touch on clients that have already installed the package via Group Policy.
The first step in deploying an MSI through GPO is to create a distribution point on the publishing server. This can be done by post-obit these steps:
- log on to the server every bit an Administrator user
- create a shared network folder (this folder will incorporate the MSI package)
- gear up permissions on this binder in order to allow access to the distribution package
- re-create the MSI in the shared folder
1.ii Create a Group Policy Object
An MSI package is deployed (distributed) through GPO as a Group Policy Object. In lodge to create an object for your package, yous tin can follow these steps:
- click on the Start push, get to Programs, select Administrative Tools so select Active Directory Users and Computers
- correct-click your domain proper noun in the panel tree and select the Properties context menu
- select the Grouping Policy tab and click New
- set the name of the policy (for example MyApplication)
- click Properties and select the Security tab
- check the Apply Grouping Policy checkbox only for the groups to which the policy will be practical
- click on the OK button
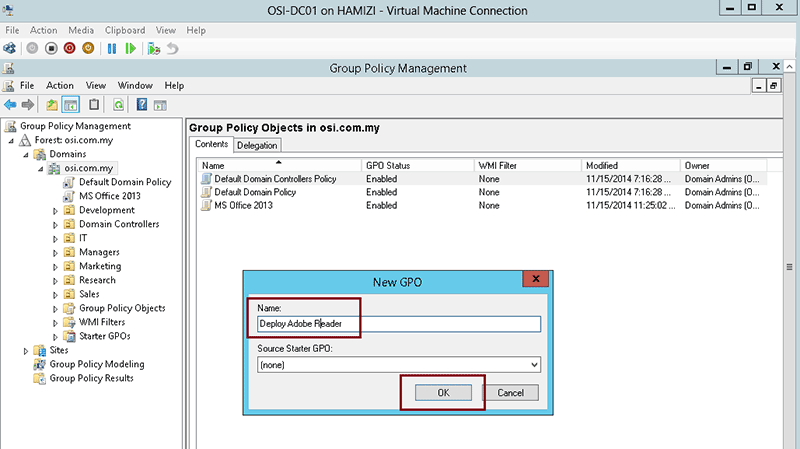
one.3 Assign an MSI package
A package can be assigned per-user or per-motorcar. Also, if the package is assigned, it will automatically be installed silently. In order to assign a packet you can follow these steps:
- click on the Start button, go to Programs, select Administrative Tools and so select Active Directory Users and Computers
- right-click your domain name in the console tree and select the Properties context carte
- get to the Group Policy tab, select the object you want and click Edit
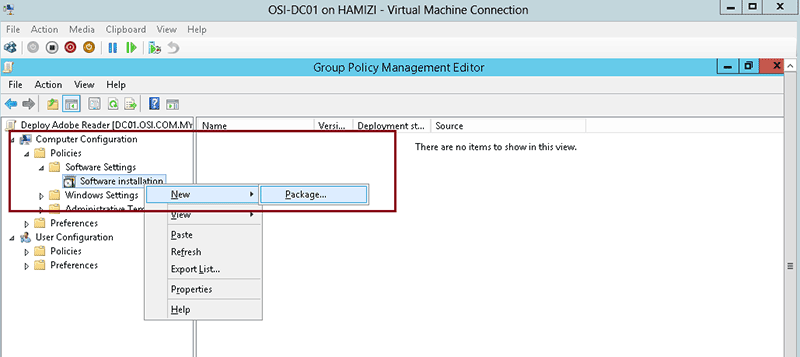
- expand Software Settings under Calculator Configuration
- right-click Software Installation, select the New context menu and so click on Package
- in the Open dialog type the full UNC path of the shared bundle yous desire to assign
- click on the Open button
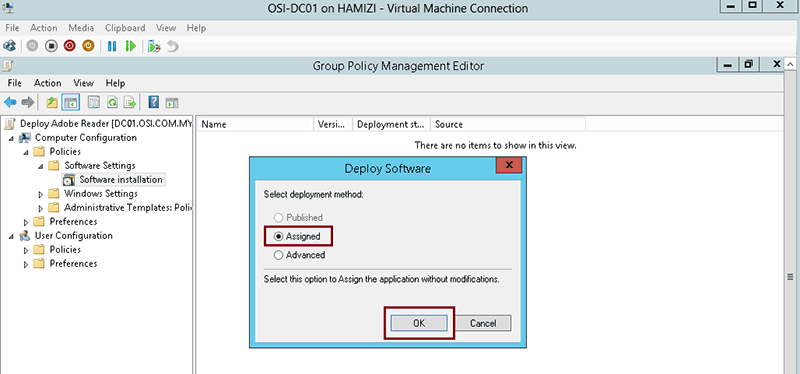
- click on Assigned and and then click OK (the parcel will exist added to the right pane of the "Group Policy" window)
- close the Grouping Policy snap-in, click OK and exit the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in
- when the client computers start, the assigned package will exist installed automatically
ane.4 Publish an MSI package
When using Group Policy, you can publish a package in gild to permit the target user to install it past using Add together or Remove programs. The steps for publishing a package are:
-
- click on the Start push button, get to Programs, select Administrative Tools and and then select Agile Directory Users and Computers
- correct-click your domain proper noun in the panel tree and select the Properties context bill of fare
- get to the Group Policy tab, select the object you desire and click Edit
- expand Software Settings under User Configuration
- correct-click Software Installation, select the New context menu and then click on Package
- in the Open dialog blazon the full UNC path of the shared package y'all want to publish
- click on the Open button
- click on Publish and so click OK (the package volition be added to the correct pane of the "Grouping Policy" window)
- close the Group Policy snap-in, click OK and leave the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in
- test the packet:
 |
| gpupdate /foce |
-
- log on to the target computer
- click on the Start button and go to Command Panel
- double-click the Add or Remove programs applet and select Add together New Programs
- in the Add programs from your network list select the program yous published
- employ the Add button to install the bundle
- click OK and then Close
1.five Redeploy an MSI package
Sometimes you may demand to redeploy a package (for example when doing an upgrade). For redeploying a parcel y'all tin follow these steps:
- click on the Start button, go to Programs, select Authoritative Tools and then select Active Directory Users and Computers
- right-click your domain proper noun in the console tree and select the Properties context menu
- go to the Group Policy tab, select the object you used to deploy the package and click Edit
- aggrandize the Software Settings element (per-user or per-auto) which contains the deployed package
- aggrandize the Software Installation chemical element which contains the deployed package
- right-click the bundle in the right pane of the Group Policy window
- select the All Tasks card and click Redeploy application
- click the Yeah push for reinstalling the awarding wherever it is installed
- close the Group Policy snap-in, click OK and exit the Agile Directory Users and Computers snap-in
1.6 Remove an MSI bundle
Group Policy also allows you to remove packages which have been deployed in the past. Hither are the steps for removing a package:
- click on the Start button, go to Programs, select Authoritative Tools and and so select Active Directory Users and Computers
- right-click your domain name in the panel tree and select the Properties context menu
- go to the Group Policy tab, select the object y'all used to deploy the package and click Edit
- expand the Software Settings chemical element (per-user or per-motorcar) which contains the deployed package
- expand the Software Installation chemical element which contains the deployed package
- right-click the package in the right pane of the Group Policy window
- select the All Tasks menu and click Remove
- select from the following options:
- Immediately uninstall the software from users and computers
- Allow users to continue to use the software merely prevent new installations
- click the OK button to continue
- close the Group Policy snap-in, click OK and exit the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in
2. Deploy Software using Startup script via GPO
If the install packages are .exe and not .msi, you are non able to distribute via the normal "Computer Configuration\Policies\Software Settings\Software Installation" policy.
Hence, using a startup script nether "Reckoner Configuration\Policies\Windows Settings\Scripts\Startup" is another choice to deploy your software. However, the software should only install once and not each startup. The popular style to do it is to record the installation results in a text file, which is then read on startup and if the file exists, so don't install. Here are all steps:
YouTube GPO Startup Script Deployment Instance:
2.1 Create the Organizational Unit (OU) for each script.
two.2 Create a Grouping Policy Object (GPO) for the newly created OU.
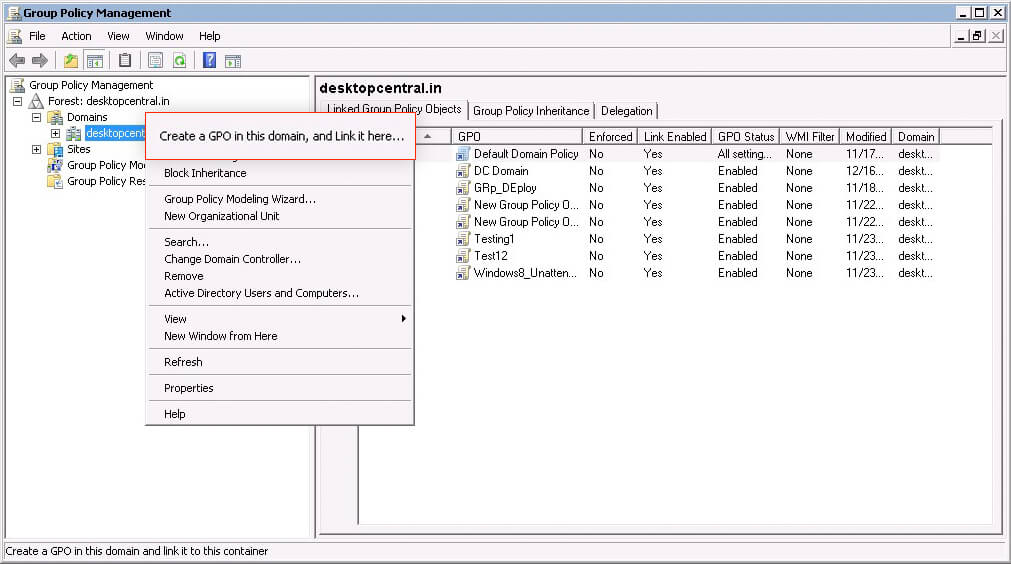
2.3 To add together the per-computer startup scripts
- Open the Group Policy Direction Console.
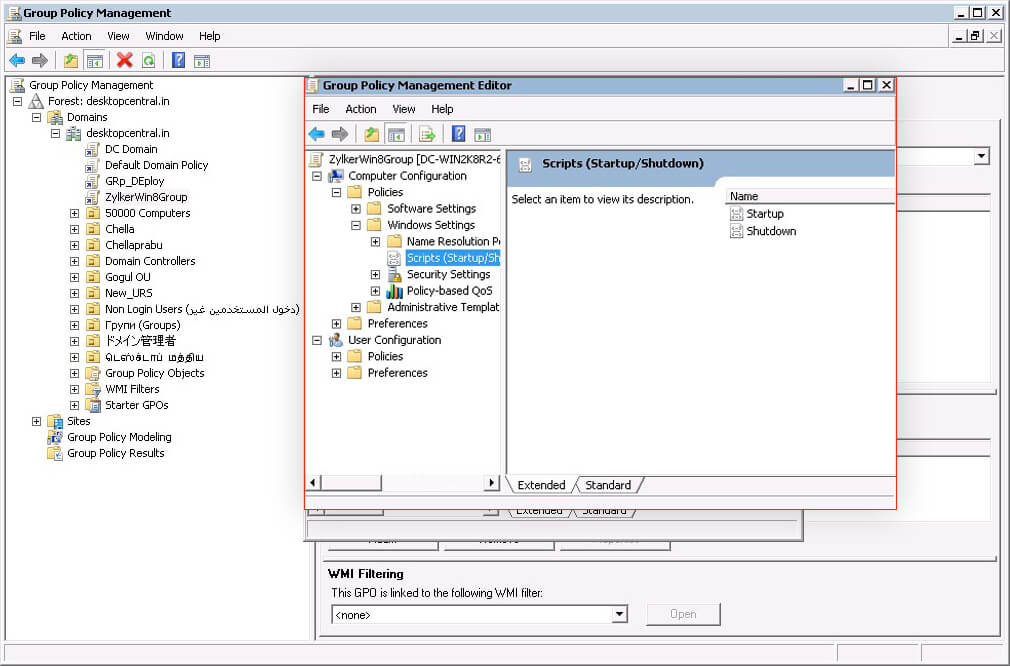
- Select Reckoner Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Scripts (Startup/Shutdown).
- In the correct-hand pane of the Group Policy Direction Console, select Startup.
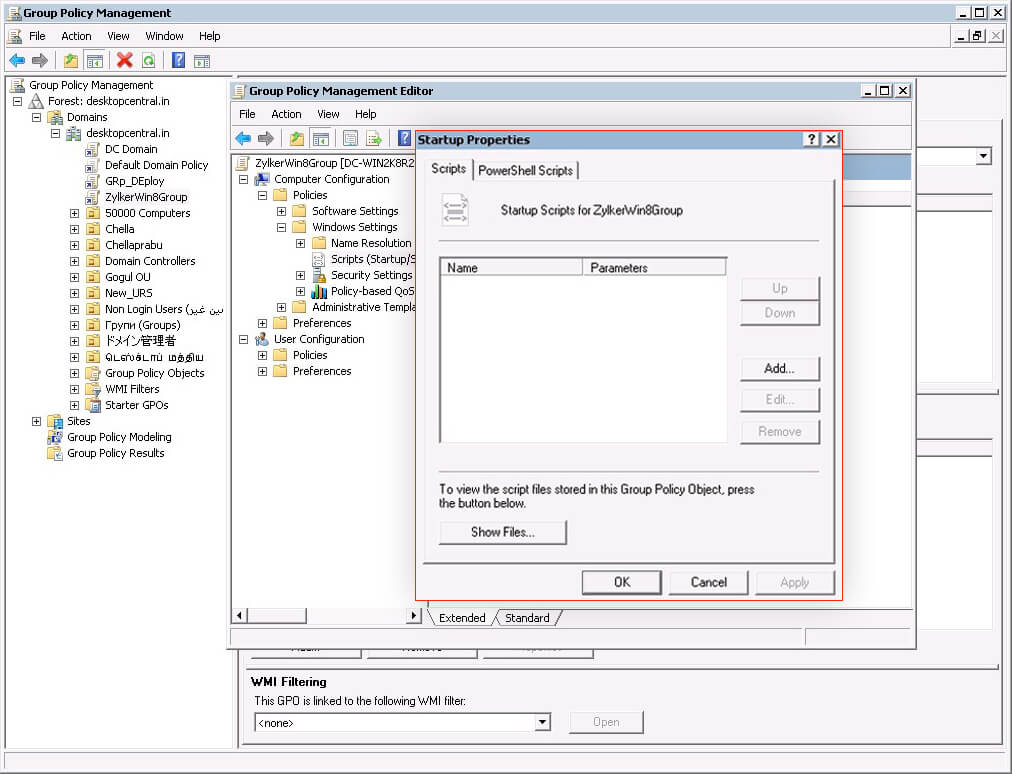
- In the Properties bill of fare, click Show Files, re-create the appropriate script to the folder displayed, and then close the window.
- In the Backdrop menu, click Add together and use Browse to find and add the newly created script.
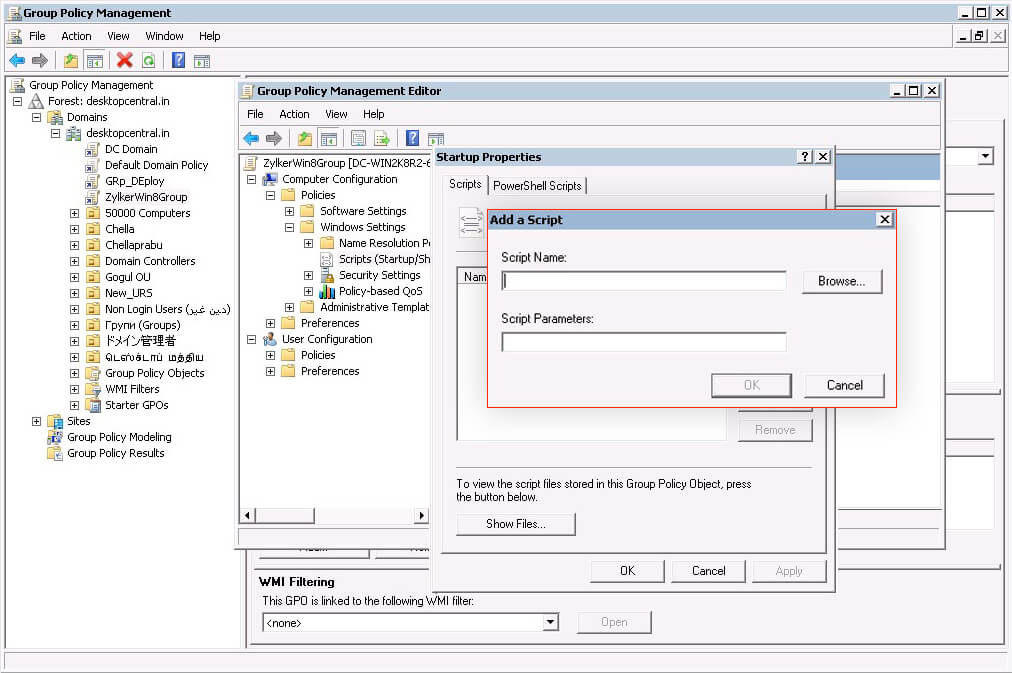
2.4 To deploy Software using Startup Script for Windows per-figurer
- Move the user devices designated to receive this deployment to the OU yous created.
- Reboot the user device and log on as any user.
- Verify that Program and Features (Add together or Remove Programs in previous Bone versions) contain the newly installed packet.
2.five To remove Software for Windows per-computer
- Move the user devices designated for the removal to the OU you created.
- Reboot the user device and log on equally any user.
- Verify that Program and Features (Add together or Remove Programs in previous OS versions) removed the previously installed package.
Script Examples:
IF EXIST "c:\vcredist_2010_x86.txt" GOTO Terminate IF EXIST "c:\vcredist_2010_x64.txt" GOTO END : 32 - scrap if exist % SystemRoot % \SysWOW64 goto 64 - bit \\servername\sharename\C ++ Redist \2 010 \vcredist_2010_x86 . exe / passive / norestart echo "Installed Microsoft Visual C++ 2010 Redistributable - x86" > "c:\vcredist_2010_x86.txt" goto End : 64 - bit \\servername\sharename\C ++ Redist \2 010 \vcredist_2010_x64 . exe / passive / norestart echo "Installed Microsoft Visual C++ 2010 Redistributable - x64" > "c:\vcredist_2010_x64.txt" : END
: 32 - fleck if be % SystemRoot % \SysWOW64 goto 64 - fleck find | reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\VisualStudio\ten.0\VC\VCRedist\x86" If not ERRORLEVEL 1 \\servername\sharename\C ++ Redist \2 010 \vcredist_2010_x86 . exe / passive / norestart goto Stop : 64 - scrap notice | reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\VisualStudio\10.0\VC\VCRedist\x64" If not ERRORLEVEL 1 \\servername\sharename\C ++ Redist \2 010 \vcredist_2010_x64 . exe / passive / norestart : END
if exist "c:\dlpagentinstalled.txt" so goto end if non exist "c:\dlpagentinstalled.txt" goto install :install msiexec /i \\win2012dc\share\AgentInstall-x64_15_5.msi /q INSTALLDIR="%PROGRAMFILES%\Manufacturer\Endpoint Agent" ENDPOINTSERVER="10.94.200.36:10443" TOOLS_KEY="63F2FFF0B6BEE4" RANDOM_KEY="B105E5B47CB88272" UNINSTALLPASSWORDKEY="7213061A9CC9AD437CEED9785" SERVICENAME="EDPA" WATCHDOGNAME="WDP" ARPSYSTEMCOMPONENT="1" ENDPOINT_CERTIFICATE="\\win2012dc\share\endpoint_cert.pem" ENDPOINT_PRIVATEKEY="\\win2012dc\share\endpoint_priv.pem" ENDPOINT_PRIVATEKEY_PASSWORD="F4569BBD5AC9DF34D6AB0BFE86365E80F0FA471F932ADD4D78D51AA35CE26038CA73B34DAB4B989C7F652CE441A4F9BBFBDA8" ENDPOINT_TRUSTSTORE="\\win2012dc\share\endpoint_truststore.pem" LOGDETAILS="Yes" /50*v %SystemDrive%\installAgent.log echo "Installed DLP Agent - x64" > "c:\dlpagentinstalled.txt" :end exit 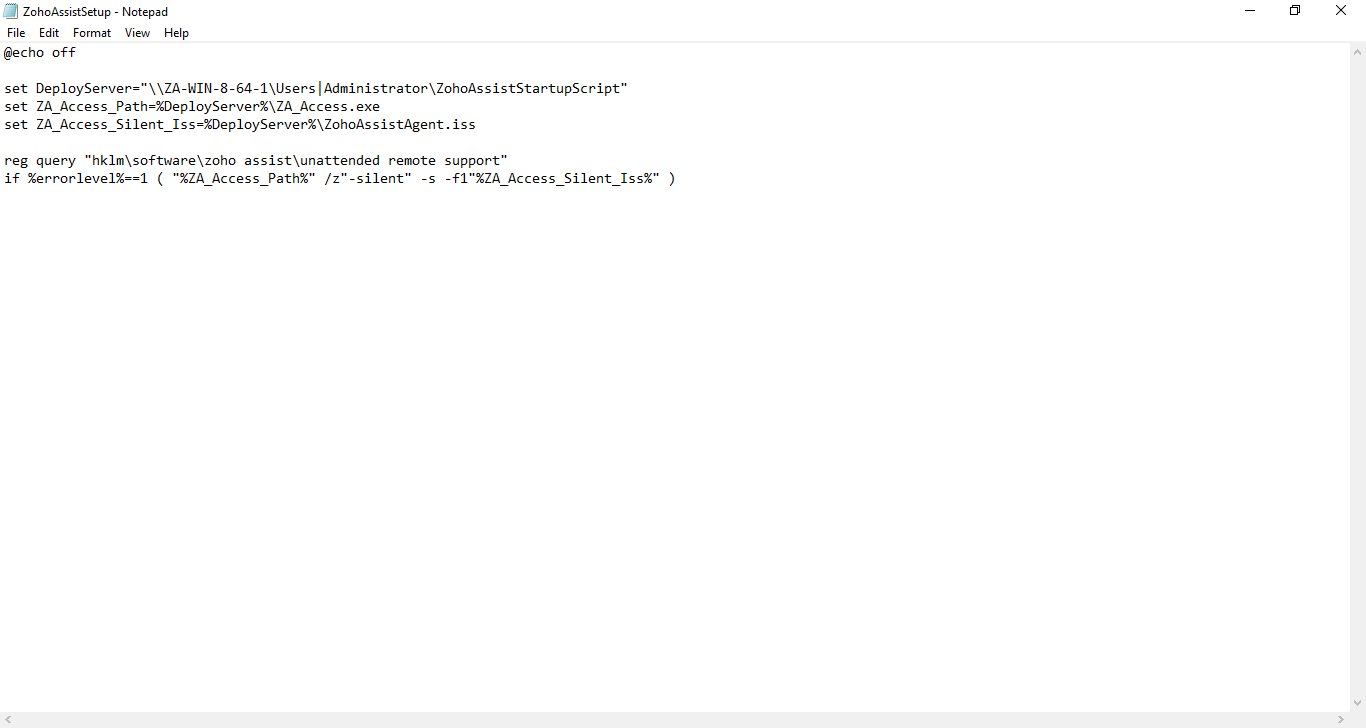
Notes:
If you would like to deploy the agent only on selected computers, follow the steps listed below, else the agent volition be deployed to all computers in your chosen domain or system unit of measurement.
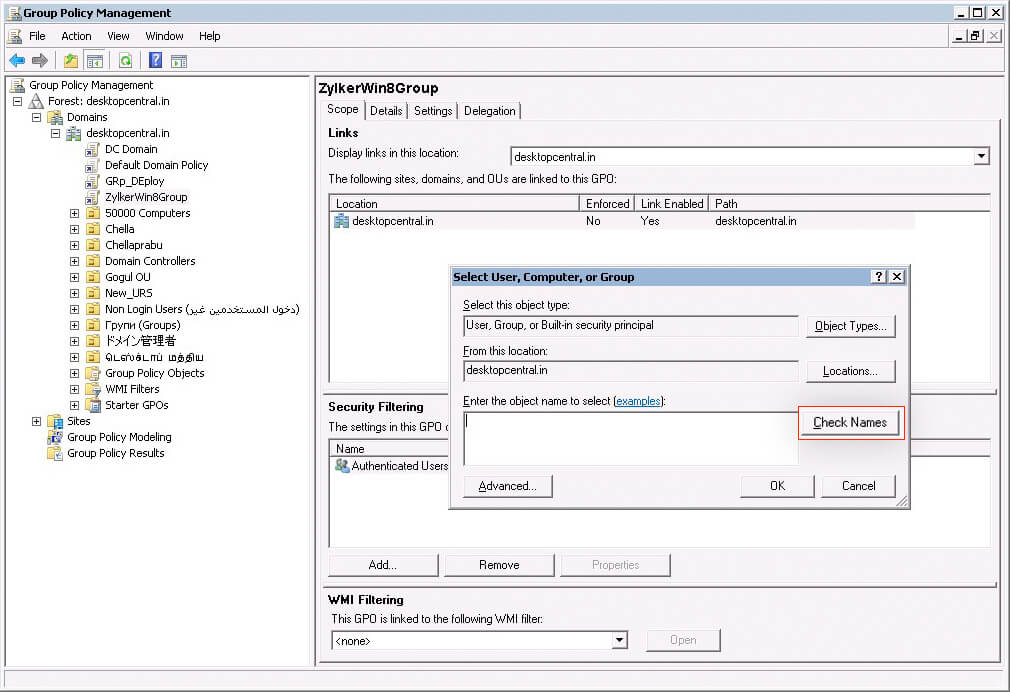
- Click Add in the Security Filtering tab.
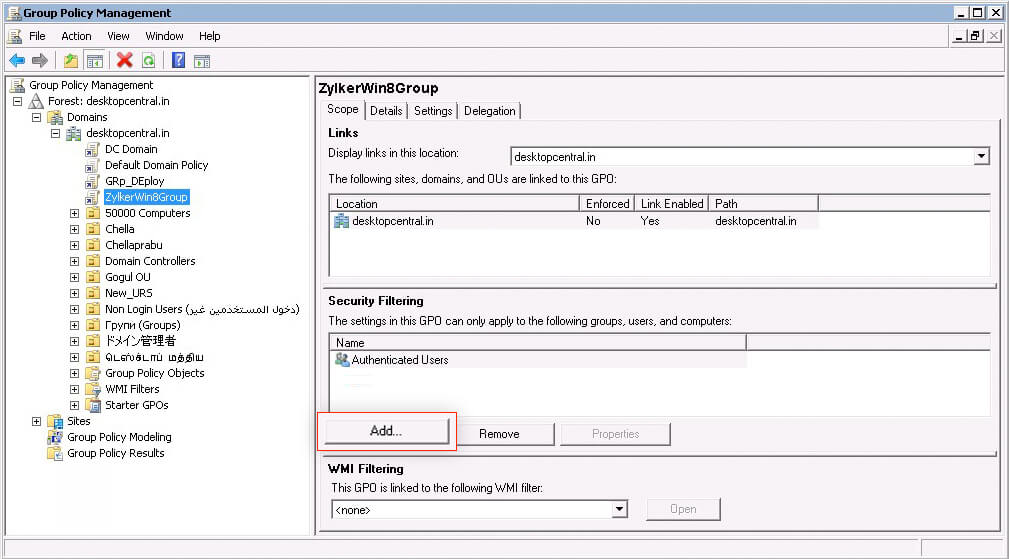
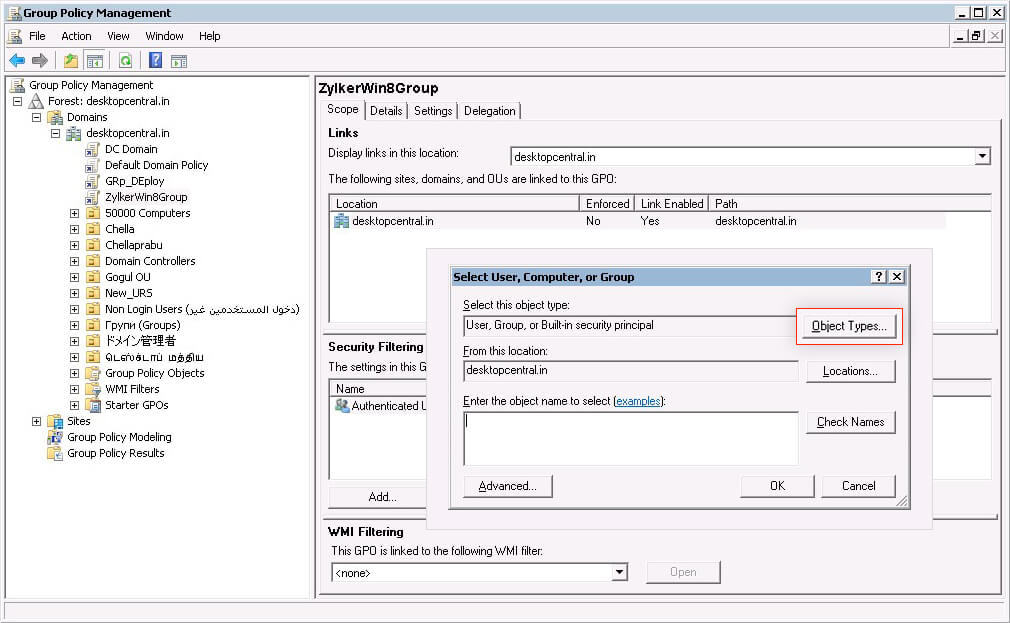
- Information technology opens Select User, Figurer, or Group dialog. Click Object Types.
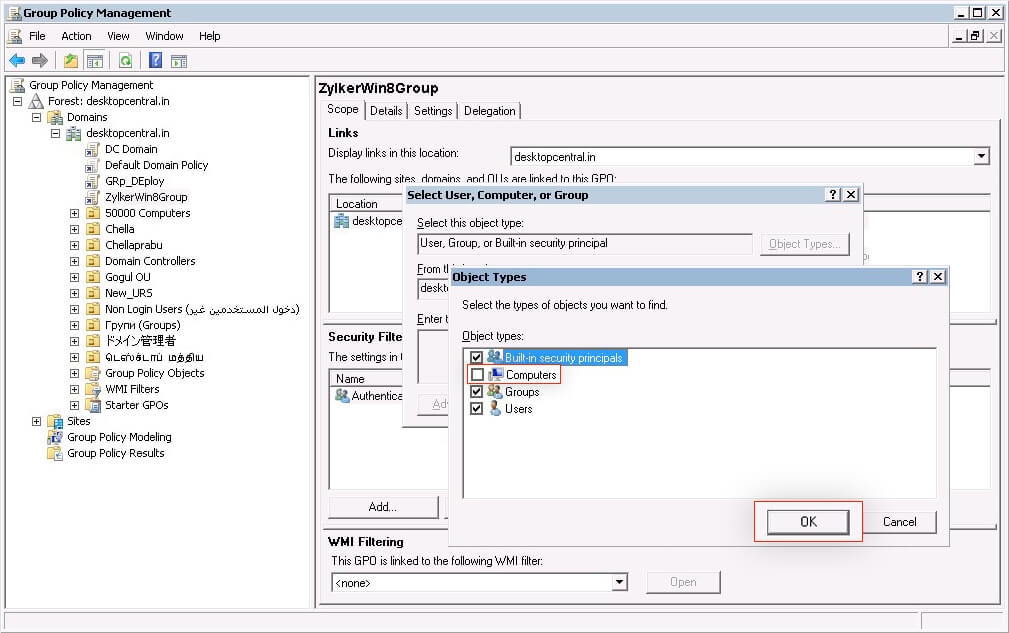
- Check Computers, and click OK.
- Enter the first few letters of the estimator name, click Cheque Names to add together computers and click OK.
References:
- Software installation startup-script via GPO
- How to utilize Group Policy to remotely install software in Windows Server 2008 and in Windows Server 2003
Source: https://www.51sec.org/2019/08/03/using-group-policy-to-deploy-software-packages-msi-mst-exe/
Posted by: lasalleflar1946.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Install Software Through Group Policy In Windows 2012"
Post a Comment